Want to use AI to forecast more confidently and accurately? With Workday Adaptive Planning’s Predictive Forecaster, you can.
This is a tool powered by time series forecasting techniques, which Senior Consultant Ted Ma shared about in the User Group for QMetrix clients.
In the below video, Ted offers insights and a hands-on example of applying predictive algorithms to real-world planning scenarios.
Predictive Forecaster: Demand Planning
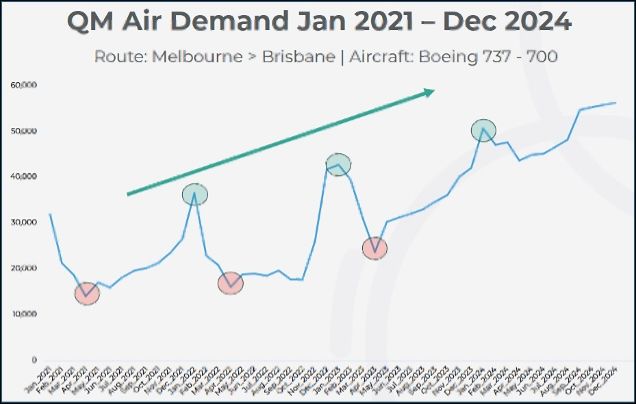
Using a demand planning model, we explored the foundational concepts of time series forecasting and highlighted other predictive models available within Workday Adaptive Planning. Of the several options, these are the two algorithms that have particular effectiveness with patterns, trends, and seasonality:
- Holt-Winters: Known for its triple exponential smoothing, which applies more weight to recent data, making it ideal for datasets with clear seasonal trends.
- Prophet: Designed to handle irregular, seasonally-driven data, offering robustness against missing data and shifts in trend.
For users uncertain about which model to select, the Autofit option can recommend the most suitable algorithm based on the dataset’s characteristics.
Note: Predictive forecasting in Workday Adaptive Planning is available only for Input Accounts on Cube or Standard sheets.
To contextualise the predictive tools, we introduced QM Air, a fictional airline company. In this session, QM Air’s Profit and Loss planning model was used, leveraging demand and total ticket revenue as key forecasting drivers.
Forecaster configuration and features
On the predictive forecaster configuration page, users can set up their forecasts. This interface also includes helpful links to documentation that explain the algorithms in greater depth.
Key features include:
- Lever Sheets: This advanced option allows users to include additional variables and drivers, enhancing the algorithm’s accuracy. It is important to note that this feature is only compatible with select forecasting models.
- Accuracy Metric: This tool estimates the reliability of the forecast as a percentage. To enable it, simply check the corresponding box in the configuration page. We recommend using this feature primarily during testing phases, as it can significantly increase processing time.
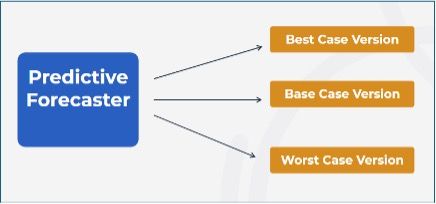
- Forecast Range: Users can enable the creation of three forecasted versions simultaneously – Base, Best Case, and Worst Case. While this feature adds valuable context to forecast planning, it may result in longer processing times due to increased computation.
Understanding the algorithms
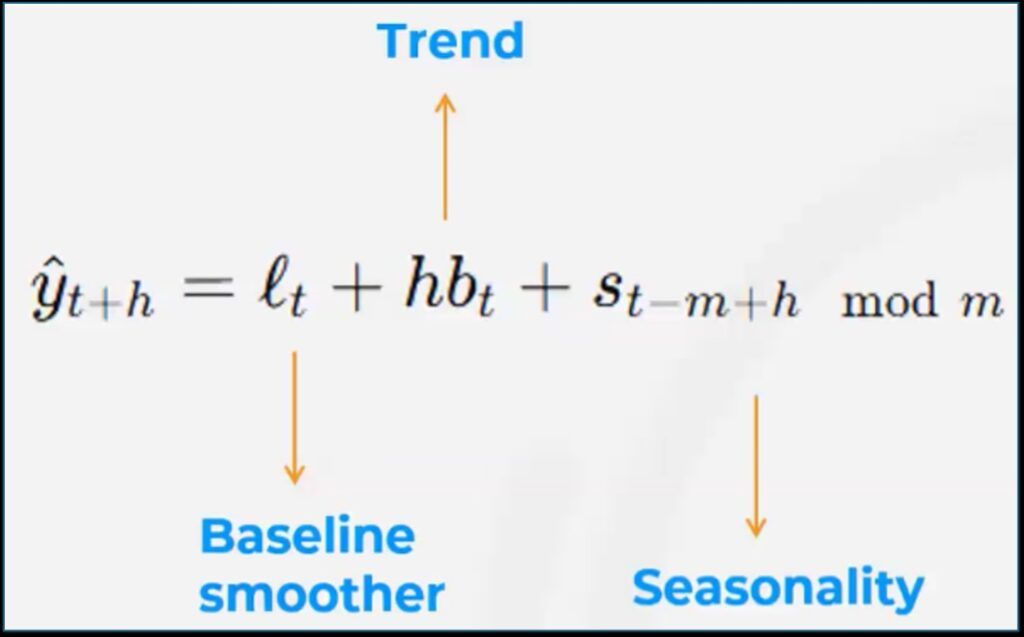
Let’s explain the fundamentals of predictive algorithms, focusing on linear regression as the core formula behind many forecasting models. Note that the linear regression formula will be rarely straightforward due to the multiple variables involved.
For instance, the Holt-Winters method includes components to account for:
- Baseline smoothing
- Trend
- Seasonality
This is a basic introduction to help users develop a better understanding of predictive algorithms so they can use the forecasting tools in Workday Adaptive Planning with greater confidence and effectiveness. If you would like to learn more, ask our team at QMetrix.
Get more Workday Adaptive Planning tips here
Workday Adaptive Planning Health Check Service
Is your Adaptive Planning instance not working for you? QMetrix provides a Health Check service to thoroughly review your instance, re-evaluate your goals and objectives, offer best practice solutions and update the Adaptive Planning solution to fit your business needs.
Find out more about the Health Check